COMPLETED MAXWELL
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD THEORY (CEMT)
Nimit Theeraleekul
B. Eng.
(June, 10, 2005, 4th revised - Feb, 1, 2012)
Download PDF File
Abstract: Maxwell electromagnetic field theory originally was born with a mechanical model of the
aether. After Einstein special theory of relativity
was accepted, the aether was rule out. Only Maxwell equations are being used
until now. Since then many important problems in electromagnetic field theory
were started, and they still can not be solved until today. Modification using ōVacuum
mechanicsö will solve all the problems and lead to a more completed theory
of electromagnetic field!
Content:
1) Introduction. 2) Original problems in Maxwell
electromagnetic field theory. 3) New model of Maxwell electromagnetic field theory. 4) Derivation of Maxwell
equations. 5) Completed
Maxwell electromagnetic field theory. 6) Electromagnetic
waveÆs radiation process. 7) Electromagnetic waveÆs radiation resistance. 8) Mechanism of light
wave. 9) Why light speed is constant? 10) What is photon rest mass? 11) Interaction mechanism between
charges particles. 12) New interpretation of PoyntingÆs vector. 13) Conclusion. 14) References.
1) Introduction This
article is the first expanding part of the original article ōVacuum
mechanics a New Approach to the Theory of Everythingö (VMTE) [1]. Because
what has been talked there about Maxwell electromagnetic field theory (EMT) is
rather a philosophical one, so in this paper it will be explained in a more
scientific detail about the improvement of EMT. But before the improvement, it
is necessary to summarize the main part of VMTE which will be involved with
EMT as below.
1.1) Vacuum medium is the fabric structure of vacuum space. This is the fundamental
hypothesis, or we could equally say that vacuum space was created from vacuum
medium. So there is no such thing which was called as empty vacuum space
(without anything), or there is no such thing like the old
familiar aether that filled the empty vacuum space. Instead there is
only vacuum space that coexists with vacuum medium, and we have called
it as vacuum medium space! Indeed it is easy to prove its existence via
a simple scientific experiment, i.e. a two-solenoid experiment [1].
In more detail, vacuum
medium is a continuous isotopic homogenous medium which have a peculiar
mechanical property. It is very thin in mass density that is ![]() (please see detail calculation in CGTR
[2]), so it is permeable by all matters almost without any observed resistance!
But it has very large elastic coefficient and sensitive to shear force (rotational
force) while not to compressive or longitudinal force.
(please see detail calculation in CGTR
[2]), so it is permeable by all matters almost without any observed resistance!
But it has very large elastic coefficient and sensitive to shear force (rotational
force) while not to compressive or longitudinal force.
Technically, Vacuum medium is the geometrical structural gravitational
potential energy; the energy that each of its infinitesimal part holds each other together by
its internal attraction force (gravity) and forming to be the physical fabric
structure of our space. If we interpret that the existing of vacuum medium
space as positive energy and its internal attraction force as negative energy,
then the total energy is zero. No vacuum medium without gravity means no space
is existed; so the principle of conservation of energy is preserved!
1.2) Electrons are tiny black holes. This is the consequent hypothesis of vacuum mechanics. To be more precise, electrons are the
condensed of vacuum medium in which each of
its infinitesimal part holds each other
together by its intrinsic gravitation force! Indeed we could prove this hypothesis
using theoretical verification by solving the problem of electronÆs mass [1]. By using the same argument as electron, we would found that
proton is also a tiny black hole but (with different size) a heavier one.
Now, what followed
from the above hypothesis is that when an electron or proton is staying still,
under this situation, it will attach the surrounding vacuum medium
(because it is something like black hole). And this will create the internal
stress in the vacuum medium around, which is appeared as electrostatic field. But when electron is moving, it will rotate in
the direction parallel to the motionÆs axis. So it will create rotational
stress in the surrounding vacuum medium while dragging it along, this is magnetostatic field!
1.3) Vacuum
mechanics -- a new conceptual mechanism for all natural phenomena.
In physics, when we deal with rigid solids,
we use the mechanics of rigid bodies as the tool. And when dealing with liquids
or gases what we used is fluid mechanics. In the same way, we will use vacuum
mechanics - the mechanism of vacuum medium when dealing with vacuum
medium. This include the interaction between condensed vacuum medium (electron
and proton) with vacuum medium, also the interaction between condensed vacuum
medium themselves.
2) Original problems in Maxwell
electromagnetic field theory. When James Clerk Maxwell first created the electromagnetic
field theory, he also invented a mechanical model of elastic solid (aether) called a granular model of space [3] for its
philosophical concept. May be because the aether concept was so strange and the
model was too complicated. And the most important point is that (at that
time) no one could prove the existing of the aether! So after Einstein had created special
theory of relativity (STR) which no need the aether, then people have
ignored the proposed model and only the equations were used until now.
Now, we could see that
the theory is limited to abstractions which using only the mathematical formula
to describe it. It is not a physical theory because there is no philosophic idea
behind for explaining how the theory works! So how could we understand
the theory without its mechanism? While we know that ōunderstandingö is
the progress of science, without it we could be mislead to something crazy. Indeed
we will see later that this is the
starting point of the problems which will follow then.
Let us start with some
familiar phenomena of electromagnetic waves. First, look for the mechanism of
electromagnetic wave propagation. It is well known that all type of waves
require some physical mediums to be the carrier which behave as the mechanism
for their propagation! But after STR had rule out the existence of the aether
that was used as the mechanism of waves, the problem was started
to occur.
Most of conventional text books have
tried to explain that electromagnetic wave could propagate by the mechanism
of itself, that is, by mutual creation between changing of electric field and
changing of magnetic field. But if we look more carefully, we will found that
it contradicts to the principle of causality because both of the generated
electric and magnetic field are created simultaneously (and also changing at
the same instance) by their common source; time-variable electric current [4].
Next problem is about electromagnetic
waves radiation process. Most of
standard text books have the difficulty for clearly explanation how the process
works [5]. Other more problem in electromagnetic field theory is about ōradiation resistanceö that will occur
during the radiation process. If we want to send radio signal via an antenna,
we have to feed electric power into the radio antenna to overcome the radiation
résistance. The question is what
resistance that we have to overcome? This was asked by Nobel Prize laureate
Richard P. Feynman [6]. Actually when we study more detail and deep in
electromagnetic field theory, we would found more and more the questions could
not be answered. And some of them will be discussed later.
Up to now, from the
above discussion we could get some clue of the problems, i.e. it is because we have
ōnothingö to deal with; ōsomethingö which acts as the mechanism
of every phenomenon that occurs in electromagnetic field theory. Someone may ask,
are we going back to old aether theory? The answer is yes and
no. Yes, we are returning to the general concept analogous to the
concept of the old aether. But no, it is not the old ether that filled vacuum
space which we want to talk about, but it is the vacuum space medium itself!
Here, armed with the new concept of vacuum mechanics -
the mechanism of vacuum medium, we will show how to solve all the problems
mentioned above. Under the concept of vacuum space medium summarized in
section 1, two essential parts are involved in electromagnetic field theory, i.e. condensed
vacuum medium ¢ electron (which play the role of tiny black hole), and
vacuum medium.
3) New model for Maxwell electromagnetic field
theory. Now, we have two main ingredients which
are involved in electromagnetic field i.e. vacuum medium and electron. While electron
(charge particle) is the generator of electromagnetic field, vacuum
medium is the mechanism for transporting the field energy. So now we are
ready to create an appropriate mechanical model for the theory. The new model proposed is the
process for flowing of direct current in a simple electric circuit as show
in the diagram fig. 1(a) below.
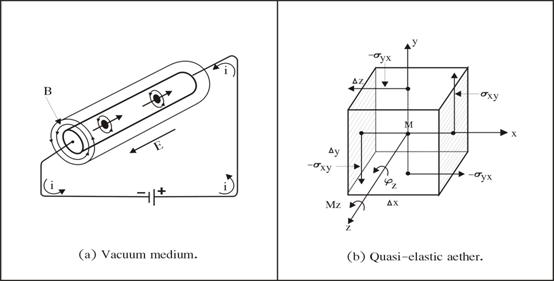
Figure 1. New model for Maxwell
electromagnetic field theory.
The new model
will follow the same concept of ōthe quasi-elastic body model of aetherö
fig. 1(b), which was developed in 19PPPPPPPPPPPthPPPPPPPPPPP century by Arnold Summerfeld [7]. The reason because the aether has
the same mediumÆs mechanical property as our vacuum medium, i.e. they are both
continuous elastic medium which are sensitive to rotation. What we will concentrate here in the new model proposed in fig. 1(a) is the flowing stream of electrons (-i) pass
through the conducting wire with negligible
resistance (for simplicity).
This was done by electromotive force provided from battery and which also
maintaining potential difference for the wire.
Remember that the
moving stream of electrons will generate electric field along the wire. And
because they also rotate while dragging the surrounding vacuum medium around the wire, this will create the rotational stress in
vacuum medium which is appeared as surrounding magnetic field B (or
H according to the
reference). In a consequent at the same time the torsion wave was generated and
propagates along the wire at a speed of light.
By the way, someone may worry about the slow flowing speed of electronsÆ
current, and how its effect could occur with speed of light. One way of
explanation is using analogy
with pressure wave occurred at the outlet of waterÆs pipe when we first turn on
the valve [8].
Anyway, it is not so good one; because it seems
to occur only at the instant which
the valve was turn on.
A better analogy for explaining the paradox is to use a row of several
pieces of metal balls hanging from a horizontal bar. If we start to swing the
first ball in the row, and when it impact the next (second) ball, at that
instant the third, the fourth and the remaining ones will stay still for
awhile. A second later, the last ball will respond the transfer series of
impact by swing away from the row.
In the analogy, metal balls represent electron particles. When the first
electron was driven by an external electromotive force and moving slowly, it
will impact the second electron, then the second electron will impact the third
electron and so on. With the series of the impact, the last electron will
respond as if it is the first electron moving with faster speed. In
conclusion the slow moving electrons could give a faster action as it was
appeared!
4) Derivation of Maxwell equations. Now we will apply the derivation
of the quasi-elastic body model of aether show in fig. 1 (b) to our vacuum
medium space. First letÆs start with the volume element ![]() of the body be twisted through the angle φ with a moment,
of the body be twisted through the angle φ with a moment,
![]() ģģ (a)
(Where k = twist modulus of vacuum medium)
ģģ (a)
(Where k = twist modulus of vacuum medium)
Because the quasi-elastic body is sensitive to rotation and the rotation has the
character of an antisystemmatic tensor. Then we get shear stresses
![]() ģģģģ (b)
(Where i, k run for x, y and z)
ģģģģ (b)
(Where i, k run for x, y and z)
From (a) and (b), stress-rotation relation in the figure is
![]() ģģģ. (c)
ģģģ. (c)
The
moments originate at the two z-surface is
![]() ģģģ.(d)
ģģģ.(d)
And the moments originate at the two y-surface is
![]() ģģģ.(dÆ)
ģģģ.(dÆ)
So the
total moment is in fact that of (a). By rotation of the letters we obtain from
(c)
![]() and
and ![]() ģģģ.(e)
ģģģ.(e)
Now we got the equation of the quasi-elastic body of vacuum medium as
![]() .
.
Or in vector form, ![]() ģģ
(f)
(Where ρ = vacuum medium density)
ģģ
(f)
(Where ρ = vacuum medium density)
This is the equation
of motion of vacuum medium. When it is
supplemented by the relation between the velocity v and the angular velocity w
which reads
![]() ģģģģģ (g). (Where
w =d Φ / d t was replaced by ∂ Φ / ∂ t.)
ģģģģģ (g). (Where
w =d Φ / d t was replaced by ∂ Φ / ∂ t.)
With the additional
assumption for the incompressibility of the vacuum
medium and note that Φ, being the curl of the displacement vector, has no divergence.
Thus v and Φ are subject to the
condition
div v =
0 ģģģ(h)
div Φ = 0 ģģģģ (k)
From Maxwell equations
in free space, we get
![]() ģ. (fÆ),
ģ. (fÆ), ![]() ģģ(gÆ)
ģģ(gÆ)
div E = 0 ģģģ.ģ (hÆ)
div B = 0 ģģģ(kÆ)
Comparing
(f), (g) (h) and (k) to (fÆ), (gÆ) (hÆ) and (kÆ), we found that they are identical! And if
we continue to work out more, we will finally get the result - the velocity of light in the vacuum medium as
![]() ģģģ. (m)
ģģģ. (m)
(Where ![]() = permeability and
= permeability and![]() = permittivity of vacuum medium.)
= permittivity of vacuum medium.)
Next to get the complete equations for
our new model, we must include electric current density j from energy
source which provide the applied toque. And referenced to the explanation for
electrostatic field and magnetostatic field in section 1.2, then for
electrostatic field (internal stress in the surrounding vacuum medium) that was
created from electric charge q (tiny black hole). According to Gauss
law, then we could interpret it as
div E = q ģģģģ..(n)
(where q = enclosed charge)
From AmpereÆs
law, the magnetostatic field (rotational stress in the surrounding vacuum
medium) is created from the moving electric charge (tiny black hole). This
could interpret it as
curl B = j ģģģģ.. (o) (where j = electric
current density)
When we combine
(fÆ) and (o) then what we got is
![]() ģģ.(p)
ģģ.(p)
Finally, we could see
that equations (gÆ), (kÆ), (n) and (p) are the
complete set of Maxwell equations!
5) Completed
Maxwell electromagnetic field theory. Up to now we have improved the
conventional Maxwell electromagnetic field theory to be a more complete theory
which is more rational and understandable. Also we could see
that all
electromagnetic field phenomena are the appearances of the dynamics action between electron and
vacuum medium. It is a part of the
mechanism of vacuum medium (vacuum mechanics), and so we should call it as ōvacuodynamicsö! Now we are ready to solve the problems in the electromagnetic
field theory mentioned early.
5.1)
Continuous wave vs. wave packet. Before going into detail with electromagnetic
waves, let us talk about one of its important characteristic. Normally when dealing with
electromagnetic waves which include radio waves, light wave etc., it seem at
first that all are continuous wave as shown in diagram fig. 2(a) below. But if we observe carefully we would
found that there is also a short portion of wave train which was called ōwave packetö as shown in fig. 2(b).
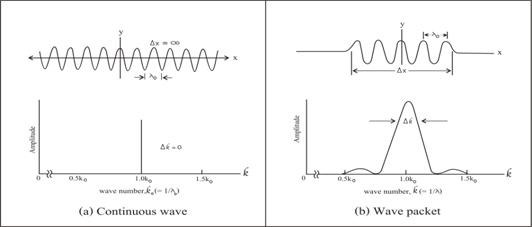
Figure 2. Two
types of natural waves.
Note that a continuous wave has a sharply defined wavelength ![]() and a
corresponding sharply defined wave number
and a
corresponding sharply defined wave number ![]() . There is
nothing about this wave that suggests the localization in space that associate
with the word ōparticleö. Instead, wave packet could be created by adding sine wave
with properly chosen wave numbers, amplitudes and phases.
. There is
nothing about this wave that suggests the localization in space that associate
with the word ōparticleö. Instead, wave packet could be created by adding sine wave
with properly chosen wave numbers, amplitudes and phases.
This collection
of infinite
waves adds to make a sine wave over a certain region of width ∆x and, by destructive interference,
adds to zero everywhere else. The prize we have paid is the sacrifice of the ōpurityö of our original wave because the
packet now no longer contains a single wave number ![]() but rather a spread of wave
numbers center about
but rather a spread of wave
numbers center about![]() .
.
For mechanical wave such as water wave, it is easy to see
both types of waves. Wave packet could be created by applying a short duration of
the disturbance source such as dropping a stone in water. But if we dip a vibrating folk in
water, the created waves will be a continuous wave train.
For electromagnetic
waves, there are both continuous waves and wave packets. Normally radio waves which are man-made waves are continuous waves, while light waves which are occurred in nature are wave packets which were called as ōphotonsö.
Next sections we
will see how continuous electromagnetic wave was generated by manmade, while light wave packet was created by nature, i.e. the mechanism of light!
6) Electromagnetic waveÆs radiation process. For the new model in section 4, we have seen how the flowing stream of electrons creates
magnetic field around and electric field the conducting wire. Now if the supply power source is a
high frequency generator instead of a battery as show in the diagram fig. 3(a). The flowing up and down of electronÆs
stream will generate waves in vacuum medium around the antenna conductor and then moving away from the wire as
shown in fig. 3(b). This is the radiation process of
electromagnetic waves.
In more detail, the
antenna conductor used above is a half-wave (of the radio frequency) length and which was called a
half wave dipole radio antenna. So the overall electromagnetic waves power
radiation field pattern is a donut shape as shown in fig. 3(c). In the next section we show how to
calculate the total power of radiation field
pattern.
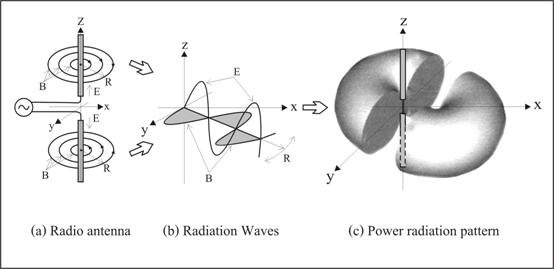
Figure 3. Electromagnetic
waves radiation process.
7) Electromagnetic waveÆs radiation resistance. Up to now we could see that electromagnetic wave was created by
disturbance of vacuum medium around the antenna, and then propagating away. It
is the oscillation; the dynamic stress ¢ stain relation within vacuum
medium. To do this, some power must be used to overcome the radiation resistance
due to the resistive action of vacuum medium. And to find the value
of the radiation resistance of the antenna, we have to calculate its radiation
power first as below.
Mathematically we say
that the radiated electromagnetic field is the tensor field (stress
tensor) or PoyntingÆs vector of vacuum medium. Below is the summary for
its derivation referenced to the book [9]. (Actually we could found it in most
text book for radio communication.)
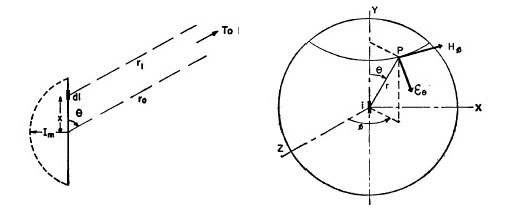
We start with the supplied current ![]() to the antenna as shown in fig. 4(a). [Where x has values from 0 to ± λ/4.] The magnetic field at
P due to current i in the element dl
is,
to the antenna as shown in fig. 4(a). [Where x has values from 0 to ± λ/4.] The magnetic field at
P due to current i in the element dl
is,
![]() ģ.. (1)
ģ.. (1)
|
(a) Half-wave dipole
antenna.
(b) Coverage of radiation field. |
Figure 4. Radiation field of half-wave dipole antenna.
Then the total magnetic field at P is, 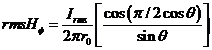 ģģģ (2)
ģģģ (2)
Also the total electric field at P is
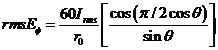 ģģģģ (3).
ģģģģ (3).
Finally the total
electromagnetic field at P is
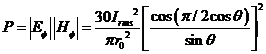 ģ (4).
ģ (4).
This is the calculated total value of radio waves radiation pattern for a
half wave dipole antenna as shown
in fig. 4 (b). Then the total power W radiated from the antenna could be
found by integrating the close surface for P, and the result is
![]() wattsģģģģ. (5).
wattsģģģģ. (5).
Finally,
to get the radiation resistance, because the calculated power in any
electrical circuit is equal to the resistance times the square of flowing
current, then for a half-wave dipole antenna in (5), the radiation
resistance is 73.26 ohms. (Actually the true value is a little higher due
to the resistance of the antenna conductor.)
8) Mechanism of light
wave. Now we will talk
about light wave packet ¢ photon, in which we have learnt that conventionally it is emitted from an exited atom. Anyway,
it still not clears how it works in detail. And to see the problem, let us start with the conversation between
Richard P. Feynman and his father in
ōThe Physics Teacherö (September 1969) about
light [10] as follow;
[My father] said, ōI understand that they say that light is emitted
from an atom when it goes from one state to another, from exited state to a
state of lower energy.ö I said, ōThatÆs right.ö
ōAnd light is a kind of particle, a
photon, I think they called it.ö I said, ōYes.ö
ōSo if the
photon comes out of the atom when it goes from the exited to the lower state, the
photon must have been there in the exited state?ö I thought a few minutes
and I said, ōI am sorry; I donÆt know. I canÆt explain it to you.ö
What we learnt from the conversation is the knowledge that ōfrom
where that light is originatedö and also the problem that ōhow light
is originatedö! Now we will discuss in more detail as follow.
First of all, let us start with the topic ōmomentum
of lightö by Richard P. Feynman [6Æ] as follow. In diagram fig. 5(b),
suppose light is coming from a source and is acting on an electron charge
q with its electric field E component and driving it
up and down with velocity v. Then magnetic field B
component (which is right angle to the electric field E) will act
on the moving electron and create the resultant force F. This
driving force F is in the direction of the propagation of light
and was called ōradiation pressureö or light pressure!
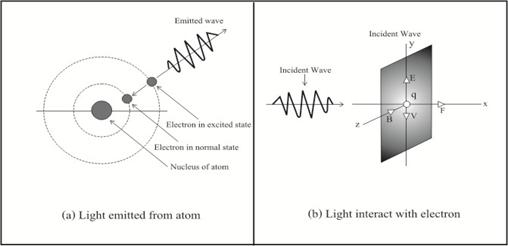
Figure 5. Mechanism of light waves.
Next we
know that the radiation pressure is F = qvB. But because
everything is oscillating, then the radiation pressure is also the time average
of F is < F>.
And because B = E/c, so <F> = q<vE>/c! Remember that the charge q times the field E is the electric
force on the charge, and the force on the charge time the velocity v is the work dW/dt being done on the charge! Therefore the ōpushing momentumö that is delivered per second by the light,
is equal to 1/c time the energy absorbed from the
light per second!
In any
circumstance where light is being absorbed, there is a pressure. The momentum that light delivers is always equal to the energy
that is absorbed, divided by c. And we already know that light carries energy. Also we now understand that it is also carries momentum, and further, that the momentum carried is always 1/c
time the energy as
![]() [Here we replaced the symbol of the
energy W with E]
[Here we replaced the symbol of the
energy W with E]
Finally
when light is
emitted from a source there is a recoil effect: the same thing in reverse. If an
atom is emitting an energy E in some
direction, then there is a recoil momentum p = E/c.
Now, we are ready to explain how light is emitted from an atom by using vacuum medium wave packet. In diagram fig. 5(b), when an
electron (in an atom) was hit by a photon (or any
other kinds of electromagnetic waves which energy is big enough), it will moves from normal state of lower energy to excited
state of higher energy. After the collision, the exited electron
will jump back from unstable excited state to its normal lower stable state
immediately. Because the ōtransition timeö is very short (1.6 nanosecond
for hydrogen atom [11]), then the jumping back electron will transfer its impulse
forceÆs energy to the surrounding vacuum medium. This makes the
disturbed vacuum medium oscillates and radiate out as a ōwave packetö of
light wave which was called photon as shown in fig. 5(a)! (Note that
this is the reverse process mentioned
in the previous paragraph.)
9) Why light speed is constant? In section 4 the velocity of light in the vacuum medium
was derived as
![]() ģģģ. (m),
ģģģ. (m), ![]() ģģģ. (mÆ)
ģģģ. (mÆ)
(Where ![]() = permeability and
= permeability and![]() = permittivity of vacuum, k and ρ are twist modulus and
density of vacuum medium.)
= permittivity of vacuum, k and ρ are twist modulus and
density of vacuum medium.)
We knew from Maxwell
electromagnetic field theory that both![]() and
and![]() in (m) are empirical constant. But both of
them are just the proportional constant that occurred in Maxwell
equation (fÆ) and equation (gÆ), in which it does not tell us why they must
be constant!
in (m) are empirical constant. But both of
them are just the proportional constant that occurred in Maxwell
equation (fÆ) and equation (gÆ), in which it does not tell us why they must
be constant!
Instead, according to the concept of vacuum medium which was
assumed that it is isotopic and homogenous, so both k and ρ are constant. Then
what follow from (mÆ), is that the velocity of light wave c must also
be constant! This is the same thing as the velocity of other natural wave,
such as sound wave for example, which is constant due to the uniform density of
the medium air.
Finally, we often heard
that vacuum medium should be very rigid for creating such a huge speed c
of light! This idea comes from the concept that sound speed in rigid medium
such as steel which is greater than the non-rigid medium such as air, for
example. But this is not quite right; the better method is to compare the same
kind of medium, such as normal air and hydrogen. For airÆs mass density![]() which has sound speed 331m/s, while
hydrogen mass density
which has sound speed 331m/s, while
hydrogen mass density ![]() has sound speed 1284m/s. The reason
is because mass density of hydrogen is lighter than the air (assumed both have
the same modulus), so its sound speed is higher than air according to wave
speed formula (m) which equal to square root of modulus over density.
And because vacuum mediumÆs density is very dilute
has sound speed 1284m/s. The reason
is because mass density of hydrogen is lighter than the air (assumed both have
the same modulus), so its sound speed is higher than air according to wave
speed formula (m) which equal to square root of modulus over density.
And because vacuum mediumÆs density is very dilute![]() , so it is not surprise that light wave
speed in vacuum medium must be very high speed!
, so it is not surprise that light wave
speed in vacuum medium must be very high speed!
10) What is photon rest mass? Again this is another problem of photon which was arisen
because modern physicists do not accept that light (photon) is the wave packet
of vacuum medium. Armed with our
new concept, it is easy to understand the
reason why photon has no rest mass while it cannot stop from traveling (propagation) with speed c.
As mentioned early that all kind of natural wave is the vibration
of some kind of physical medium, for example sound wave is the vibration of air. And it is easy to
understand that a pulse of sound wave (analogous to photon) also has no rest mass too. The reason is
because the vibration of air create sound wave that traveling from its source; staying still
of sound wave means no vibration or no
sound wave (then no rest mass exist). Indeed, all other kind of natural wave
such as water wave, including light wave (photon) cannot stop (no vibration) and has no rest
mass!
11) Interaction mechanism between charge
particles. Up to now, in
order to give us some confidence in the concept that charge particles are tiny
black holes (mentioned early), we will use it to explain how the interaction
between charge particles work. Conventionally ōdifferent type of charge particles attract,
while the same type of charge
particles repelö, but there is no
explanation why?
Armed with
the concept of tiny black hole, it is easy to understand the interaction, but
in a different view which is more reasonable, that is ōdifferent size of charge
particles attract, while the same size of charge particles repelö.
Now let us see how the interaction mechanism works.
11.1)
Repelling between
same size charges. Actually
all sizes of black holes must attract each other. This is what Richard
P. Feynman told in his book [12], in which he observed that proton and
proton attract each other when they are separate at some distance apart!
But when they are close together less than a certain distance then they
will repel each other, anyway he did not say why it is so!
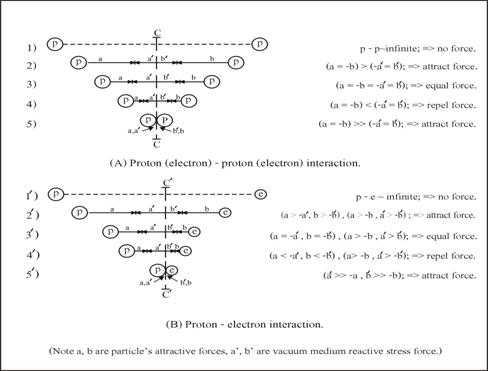
Figure 6. Interaction mechanisms between charges particles.
The reason that there
are two types of the interaction between charge particles (tiny black holes)
is because they all are immerged in vacuum medium, and how the existing
of vacuum medium is the cause of the repulsion between the same sizes of tiny
black hole which will be explained below.
According to diagram
fig. 6(A) it is the interaction between proton and proton or between
electron and electron. Cases (1) when the separate distance is infinity, no
interaction force between them appear. Case (2) when they are closing together,
they begin to attract each other because both of them are tiny black holes.
Case (3) at a certain distance where the attractive forces of the black
holes is equal to the repulsive force of the internal stress in vacuum medium
between them (because black holes create internal stress in the vacuum medium
around), then they stop to attract each other. Cases (4) when the
separated distance is closer than in (3), then they repel each other. This is the phenomenon we are familiar, i.e. same type of charges repel! Case (5) when both
particles are forced to stick together, that is the attract force of the black
holes is greater than the reaction force of the internal stress in vacuum
medium. This is how two or more proton particles could stay in an atom nucleus.
(Note, the vertical
line c ¢ c is perpendicular and divide into two half of the line joint between
p and p, while the line cÆ ¢ cÆ in (B) is closed to e than p due to their
different size.)
11.2)
Attraction
between different size charges. In
(B), it is the interaction between proton and electron. Case (1Æ) and
(2Æ) are the same situation as (1) and (2) in (A). Case (3Æ) is the same as in
(3) (A), but the only different is the separate distance between p and e which
is smaller than in (3) (A). The reason is because of the different size between
proton and electron. And this is the
phenomenon we are familiar, i.e. different type of
charges attract. Case (4Æ), when the separated distance
is closer than in (3Æ), then they begin to repel each other as in case (3) (A).
Case (5Æ), it is the same situation as (5) in (A), and what we got is a
neutron!
12) Problems involved PoyntingÆs vector. Poynting vector S, is a very important concept when we work
with the flowing of electromagnetic field energy. It tells us the rate at which
the field energy moves around in space. Indeed all radio wave transmission
energy is calculated using this concept as was shown in section 7! Anyway, when working with it in some
particular cases, we would found that we
are facing with some crazy problems [11Æ]!
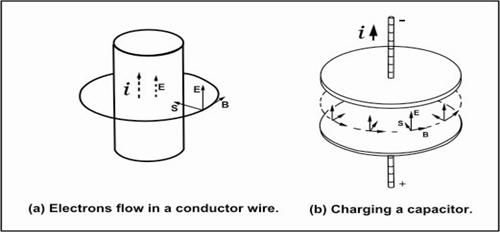
Figure 7. Problems involved
PoyntingÆs vector.
According to the conventional
concept of Poynting vector, such as heat dissipation energy in a conductor
wire, it is not come from the flow-in electron current; instead it comes from
the field energy around the wire as show in diagram fig. 7(a). Another example
is the charging energy to store in a capacitor is not come from the flow-in
electron current; instead it comes from the field energy around the capacitor
as show in diagram fig. 7(b). These problems arise because of the ambiguity of
the field, i.e. we do not know what really electromagnetic field is!
12.1) Conventional interpretation of PoyntingÆs
vector. Before solving the problems by using our new concept of vacuum
mechanics, we will first see detail how modern physics understand (or ¢ not
understand?) and work out the electromagnetic field energy by using Poynting
vector concept as follow.
First
let us consider diagram fig. 7(a), which shows a current i flow through
a conductor wire length l, with internal resistance R. And to
produce the current, we need an electric field E parallel to the wire of
magnitude iR/l. Also we have
learnt early that when electrons (current) move, they will also rotate and
create magnetic B around the wire according to the application of Biot ¢
Savart law i.e.
![]() [Where r is the wire radius of the wire]
[Where r is the wire radius of the wire]
Now according to Poynting vector, ![]() is the energy (per unit area per second)
flows in the wire from outside around the wire.
is the energy (per unit area per second)
flows in the wire from outside around the wire.
Then
the total energy around the wire which flows in it is equal to the heat
dissipate from the wire resistance,
![]()
So it was concluded that the heat dissipate from the wire resistance is
not coming from the input current, instead it comes from the flow in energy
around the wire!
Next
let us consider diagram fig. 7(b), a capacitor being charged slowly. There is a
nearly uniform electric field inside which is changing with time. At any
instant the total electromagnetic energy in the capacitor is
![]() ģ (1).
ģ (1).
(Where a = radius, h
= plateÆs separation of the capacitor.)
And the rate of receiving energy of the
capacitor
![]() ģ (2)
ģ (2)
Now when the capacitor is charging, there is a magnetic field that
circulates around the axis. And by using one of Maxwell equations, the
circulate magnetic field is given by
![]() , then
, then![]() ģģ (3).
ģģ (3).
Using Poynting vector (S), it
seems that the receiving energy is flowing in from space around. Then the
rate of the flowing in energy through the surface area of 2¶ah is
![]() ģ (4).
ģ (4).
That is, it is equal to (2). And conventionally it was explained
that the flowing of electromagnetic field energy into the capacitor comes from
space around it (not the current from input). Of course we knew that it is
not true!
12.2) New interpretation of PoyntingÆs vector. To solve the problems involved Poynting vector concept, first
let us first go back to our proposed new model of Maxwell electromagnetic field
which is the process for flowing
of direct current in a simple electric circuit as show in the diagram
fig. 1(a) in section 3.
Remember that
electrons are tiny black holes, so when they are moving they will rotate and drag the surrounding vacuum medium around the wire. This will create rotational stress in
vacuum medium which is appeared as the surrounding magnetic field B. Also since the wire has resistance, then
there is an electric field along it for driving the current. And because there
is a potential drop along the wire, there is also an electric field E just outside the wire and parallel to the
surface.
Now come to the crucial
point which mislead to the crazy problems mentioned above; it is the
direction of Poynting vector S which point toward the wire, and then it
was interpreted as the energy flow into the wire. The reason of the
misinterpretation is because modern physicists do not understand what really
the electromagnetic field energy is!
To
solve the problem of the conductor wire, it is easy by using our new concept
that electrons are tiny
black holes. Because the electrons will attract the
surrounding vacuum medium and creating compressive rotational stress in the medium, which is then manifest as electromagnetic energy around the wire. And according to the compressive rotational stress, its direction is
point toward into the wire, not outward as the
conventional interpretation. In conclusion, the flow-in current (of
electrons) give rise to the dissipate heat energy while create the surrounding
electromagnetic energy around the wire!
Finally,
to solve the problem of the capacitor, we will use our new concept that electrons are tiny black holes in the same way as was done with the conductor wire. But
because the dissipate heat energy and the surrounding electromagnetic energy
around the connecting wire is small (compare to the capacitor energy) so we
will neglect them.
When
the flow-in current of electrons accumulates in the upper disc plate of the
capacitor, they will create something like a rotating disc of tiny black holes.
Then the rotating disc will drag and rotate the vacuum medium between the two
plates and forming a compressive rotational stress in the medium, in which it appears
as the flow-in electromagnetic field energy as show in the diagram. In
conclusion, the flow-in current give rise to the energy store in the
capacitor, while creates a compressive rotational stress in the vacuum medium between the two plates in which it appeared as the flow-in
electromagnetic field energy into the capacitor!
13) Conclusion. Up to now we have shown how to improve Maxwell
electromagnetic field theory, i.e. we
have added a suitable model to fulfill its philosophical concept. Then the
theory is not just a mathematical equations, but it is what we could understand
how it work. So the existing problems which born in the conventional theoretical
concept could
be eliminated by using the new concept of vacuum mechanics!
Actually we could see that all electromagnetic field phenomena, i.e.
electrostatic field, magnetic field and electromagnetic field are the
appearances of the mechanism of vacuum medium ¢ vacuum mechanics. More specific,
it is the interaction between electron (condensed vacuum medium) and vacuum
medium. So more properly, we could say that the action of electrodynamics is
the action of ōvacuodynamicsö - the
dynamic of vacuum medium!
People who are familiar with Einstein special theory of relativity would
know that STR was born in order to solve some problems occurred in
electrodynamics that was not work properly in the realm of Newton classical mechanics. Anyway, we will found (in the article
ōCompleted Einstein special theory of relativity (CSTR) [13]) that STR cannot
solve all the problems in EMT, instead it give rise to some fundamental problem
which we talked early!
Anyway we could also found that what was done in this paper is not fully
mathematical rigor. But it provides some detail just enough for us to have some
confidence in the new proposed concept. And it is the starting point for
modification of the theory. So from now on, it is time for the professional
which is involved to complete it!
14) References.
(Precaution; Several text books with different
authors were used as the reference and each author used different pattern and
different notation for the same formula. Here in this paper, the author has
made some change of the original pattern and notation for the readers
convenient, so please be careful in reading!)
[1] By Nimit Theeraleekul, now presenting in www.vacuum-mechanics.com
[2] Nimit Theeraleekul, ōöCompleted
Einstein general theory of relativity (CGTR)ö, now
presenting in www.vacuum-mechanics.com
[3] James Blake Westgard, ōElectrodynamics: A Concise
Introductionö p. 90-95.
[4]
Oleg D. Jefimenko, ōCausality Electromagnetic Induction and Gravitationö Second
Edition
p. 13-16.
[5]
Constantine A. Balanis ōAntenna Theory, Analysis and Designö p.7-11.
[6]
Richard P. Feynman, Robert B. Leighton and M. Sands, ōThe Feynman Lectures on
Physicsö. Vol. 1, p.32-1 to 32-2, for [6Æ]
p. 34-10 to 34-11.
[7] Arnold Sommerfeld, ōMechanics of Deformable Bodiesö, p.108 ¢
111.
[8]
D. Halliday, R. Resnick, and K. Krane, ōPhysicsö Vol. 2 Extended Version Fourth
Edition,
p.700.
[9]
John D. Ryder, ōNetwork, Lines and Fieldsö Second Edition, p.535-548.
[10]
Peter W. Milonni,öThe Quantum Vacuum, (An Introduction to Quantum
Electrodynamics)ö, p. 77.
[11]
John S. Townsend ōA Modern Approach to Quantum Mechanicsö p.435.
[12]
Richard P. Feynman,
Robert B. Leighton and M. Sands, ōThe Feynman Lectures on
Physicsö Vol. 2, p. 8-7, for [11Æ] p. 27-6 to 27-8.
[13] By Nimit
Theeraleekul, now presenting in www.vacuum-mechanics.com
ģģģģģģģģģģ.